Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm:
How It Works and How To Tune It. 58pp
MS Word 97 or .pdf file
only $9.50.
Get more details, buy, and download
| ControlSim The PID controller and process simulator based on MS Excel spread sheets. $45.00 | Click here to get more details, buy, and download |
Buy and download my eBook: The
PID Control Algorithm: |
Get more details, buy, and download |
Chapter 1
The Feedback Control Loop
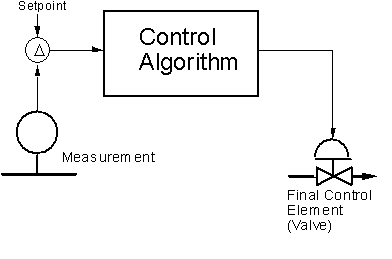
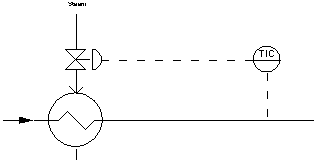
The system measures the process, compares it to a setpoint, and then manipulates the output in the direction which should move the process toward the setpoint.
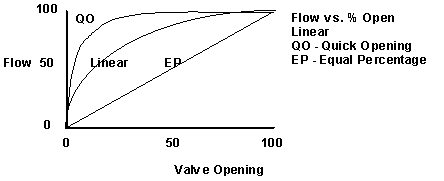
Valve Linearity
Valves are usually non-linear. That is, the flow through the valve is not the same as the valve position. Several types of valves exist:
Linear
Same gain regardless of valve position
Equal Percentage
Low gain when valve is nearly closed
High gain when valve is nearly open
Quick Opening
High gain when valve is nearly closed
Low gain when valve is nearly open
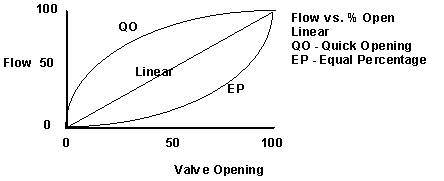
As we will see later, the gain of the process, including the valve, is very important to the tuning of the loop.
• If the controller is tuned for one process gain, it may not work for other process gains.
Valve Linearity:
Installed characteristics
The flow vs. percent open curve changes due to the head loss in the piping
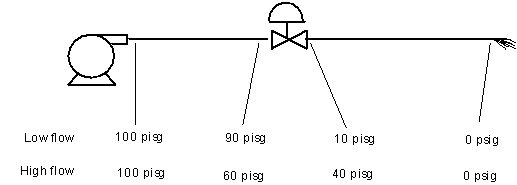
At low flow, the head loss through the pipes is less, leaving a larger differential pressure across the valve.
At high flow, the head loss through the pipe is more, leaving a smaller differential pressure across the valve.
The effect is to increase the non-linearity of most valves.
Fail Open Valves
Valves are usually either: Fail Closed, air to open or
Fail Open, air to close
• Regardless of the way the valve operates, the operator is interested in the knowing and adjusting the position of the valve, not the value of the signal. "Up is always open"
• All controllers have some means of indicating the controller output in terms of the valve position. When the operator increases the output as indicated on the controller, the valve opens.
Indication Inversion
|
The output indication is
inverted. The controller action takes the valve action into acount. The flow loop is direct acting. Most analog controllers work like this. |
Signal Inversion |
|
|
The output signal is
inverted. The controller action ignores the valve action. The flow loop is reverse acting Some distributed control systems work like this. |
go to chapter 2: the process response
Buy and download:
my 21 page e-book on the PID algorithm.
MS Word 97 format only $5.00
Detail and purchase
my 25 page e-book on the PID Tuning.
MS Word 97 format only $6.00
Both for only $10.00